

自动化运维(二)Ansible Playbook
1.Playbook剧本
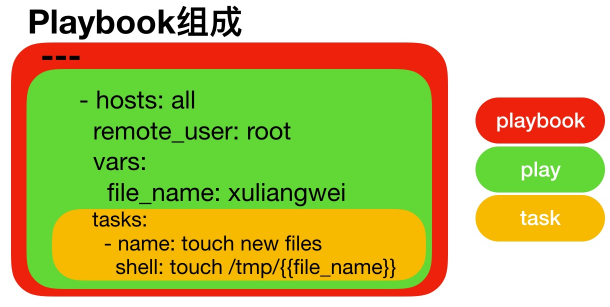
1.playbook翻译过来就是“剧本”,那playbook组成如下
play: 定义的是主机的角色
task: 定义的是具体执行的任务
playbook: 由一个或多个play组成,一个play可以包含多个task任务
简单理解为: 使用不同的模块完成一件事情
2.playbook的优势
1.功能比ad-hoc更全
2.能很好的控制先后执行顺序, 以及依赖关系
3.语法展现更加的直观
4.ad-hoc无法持久使用,playbook可以持久使用
3.playbook的配置语法是由yaml语法描述的,扩展名是yaml和yml
缩进
YAML使用固定的缩进风格表示层级结构,每个缩进由两个空格组成, 不能使用tabs
冒号
以冒号结尾的除外,其他所有冒号后面所有必须有空格。
短横线
表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。
多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一列表。
#playbook示例
[root@manager ~]# cat f1.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
file_name: xuliangwei
tasks:
- name: Create New File
file: name=/tmp/{{ file_name }} state=touch#playbook执行方式 [root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook f1.yml PLAY [all] ******************************************************************************************************************************** TASK [Gathering Facts] ******************************************************************************************************************** ok: [10.0.0.30] TASK [使用变量] ******************************************************************************************************************************* changed: [10.0.0.30] PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************************** 10.0.0.30 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
Playbook执行结果返回颜色状态
红色: 表示有task执行失败或者提醒的信息
黄色:表示执行了且改变了远程主机状态
绿色:表示执行成功
2.Playbook变量使用
Playbook定义变量有三种方式
1.playbook的yaml文件中定义变量赋值
2.--extra-vars执行参数赋给变量
3.在文件中定义变量
1、playbook的yaml文件中定义变量赋值
#playbook中定义
[root@manager ~]# cat f2.yml
- hosts: all
vars: #定义变量
file_name: bgx_yaml_vars
tasks:
- name: # {{ file_name }}引用上面定义的变量
file: path=/tmp/{{ file_name }} state=touch
#playbook执行,在/tmp目录创建bgx_yaml_vars文件
[root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook f1.yml2、--extra-vars执行参数赋给变量
#playbook中引用变量
[root@manager ~]# cat f3.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Create New File
file: path=/tmp/{{ file_name }} state=touch
#playbook执行时传入file_name变量的参数,在/tmp目录创建bgx_extra-vars文件
[root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook f2.yml --extra-vars "file_name=bgx_extra-vars"在文件中定义变量: 可以在/etc/ansible/hosts主机组中定义,然后使用palybook进行调度该变量
#在文件中定义变量
[root@manager ~]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[nfs]
10.0.0.20
[nfs:vars]
file_name=bgx_filename
#Playbook中调用该变量
[root@manager ~]# cat f4.yml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Create New File
file: path=/tmp/{{ file_name }} state=touch
#playbook执行,在/tmp目录创建bgx_filename文件如果定义的变量出现重复,且造成冲突,优先级如下:
1.extra-vars外置传参的优先级最高 [所有执行的主机都生效]
2.定义在yml文件中的优先级其次 [所有执行的主机都生效]
3.hosts文件中定义的变量优先级最低 [当前主机组定义会生效]
3.Playbook变量注册
1、注册变量: register关键字可以存储指定命令的输出结果到一个自定义的变量中
[root@manager ~]# cat f5.yml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name:
shell: netstat -lntp
register: System_Status
- name: Get System Status
debug: msg={{System_Status.stdout_lines}}
#playbook执行结果
[root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook f5.yml
PLAY [all] ********************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [10.0.0.30]
TASK [shell] ******************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [10.0.0.30]
TASK [Get System Status] ******************************************************************************************************************
ok: [10.0.0.30] => {
"msg": [
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 925/sshd ",
"tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 925/sshd "
]
}
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************************************************************************
10.0.0.30 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=04.Playbook条件语句
playbook中的条件判断语句使用when
[root@manager ~]# cat f6.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Create File
file: path=/tmp/this_is_{{ ansible_hostname }}_file state=touch
when: (ansible_hostname == "nfs") or (ansible_hostname == "backup")
#系统为centos的主机才会执行
- name: Centos Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
when: (ansible_distribution == "CentOS")
#系统为ubuntu的主机才会执行
- name: Ubuntu Install httpd
yum: name=httpd2 state=present
when: (ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu")5.Playbook循环语句
1、标准循环使用场景-批量安装软件
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Installed Pkg
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- wget
- tree
- lrzsz2、标准循环使用场景-批量创建用户
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Add Users
user: name={{ item.name }} groups={{ item.groups }} state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'testuser1', groups: 'bin' }
- { name: 'testuser2', groups: 'root' }3、标准循环使用场景-拷贝多个目录
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Configure Rsync Server
copy: src={{ item.src }} dest=/etc/{{ item.dest }} mode={{ item.mode }}
with_items:
- {src: "rsyncd.conf", dest: "rsyncd.conf", mode: "0644"}
- {src: "rsync.passwd", dest: "rsync.passwd", mode: "0600"}6.Playbook异常处理
默认Playbook会检查命令和模块的返回状态,如遇到错误就中断playbook的执行
加入参数: ignore_errors: yes 忽略错误
[root@manager ~]# cat f9.yml --- - hosts: all remote_user: root tasks: - name: Ignore False command: /bin/false ignore_errors: yes - name: touch new file file: path=/tmp/bgx_ignore state=touch
7.Playbook tags标签
1、打标签
对一个对象打一个标签
对一个对象打多个标签
对多个对象打一个标签
2、标签使用,通过tags和任务对象进行捆绑,控制部分或者指定的task执行
-t: 执行指定的tag标签任务
--skip-tags: 执行--skip-tags之外的标签任务
[root@manager ~]# cat f10.yml --- - hosts: all remote_user: root tasks: - name: Install Nfs Server yum: name=nfs-utils state=present tags: - install_nfs - install_nfs-server - name: Service Nfs Server service: name=nfs-server state=started enabled=yes tags: start_nfs-server
使用-t指定tags执行, 多个tags使用逗号隔开即可
[root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook -t install_nfs-server f10.yml
使用--skip-tags排除不执行的tags
[root@manager ~]# ansible-playbook --skip-tags install_nfs-server f10.yml
8.Playbook Handlers
playbook安装Apache示例
[root@m01 ~]# cat webserver.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
#1.定义变量,在配置文件中调用
vars:
http_port: 8881
#2.安装httpd服务
tasks:
- name: Install Httpd Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
#3.使用template模板,引用上面vars定义的变量至配置文件中
- name: Configure Httpd Server
template: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
#4.启动Httpd服务
- name: Start Httpd Server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
#5.检查Httpd服务当前的运行的端口状态
- name: Get Httpd Server Port
shell: netstat -lntp|grep httpd
register: Httpd_Port
#6.输出Httpd运行的状态至面板
- name: Out Httpd Server Status
debug: msg={{ Httpd_Port.stdout_lines }}
ignore_errors: yes
#7.如果配置文件发生变化会调用该handlers下面的模块
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
service: name=httpd state=restarted9.Playbook Include
include用来动态的包含tasks任务列表,include_tasks新版/include老版
include调用任务方式
#主入口文件 [root@mha ~]# cat main.yml - hosts: all remote_user: root tasks: - include_tasks: f20.yml - include_tasks: f21.yml #f20.yml [root@mha ~]# cat f20.yml - name: create file1 command: touch file1 #21.yml [root@mha ~]# cat f21.yml - name: create file2 command: touch file2


- 控制面板
- 搜索
- 你好,朋友
-
真是美好的一天!
- 站点信息
-
- 文章总数:90
- 页面总数:0
- 分类总数:9
- 标签总数:0
- 评论总数:0
- 浏览总数:119133
 豫公网安备41042502000209号
豫公网安备41042502000209号